Rarely are ideas born overnight. And for an idea to become a great idea, it takes considerable work and effort to develop. Part of the reason we end up with under-developed ideas is that we stick with the first good idea we have — rather than taking the time to explore complementary approaches. 6-8-5 is designed to combat this pattern by forcing us to generate lots of ideas in a short period of time. The activity can then be repeated to hone & flesh out a few of the best ideas.
Number of Players
2+
Duration of Play
5 minutes to play each round
15-20 minutes for discussion
How to Play
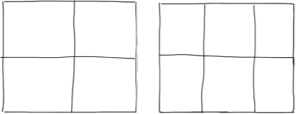
1. Before the meeting, prepare several sheets of paper with a 2×2 or 2×3 grid. You want to create boxes big enough for players to sketch their ideas in, but small enough to constrain them to one idea per box. Prepare enough paper for everyone to have about 10 boxes per round.
2. As the group is gathering, distribute sheets of paper to each player. Or instruct the group on how to make their own 2×2 grid by drawing lines in their notebook.
3. Introduce the game and remind players of the objective for the meeting. Tell players that the goal with 6-8-5 is to generate between 6-8 ideas (related to the meeting objective) in 5 minutes.
4. Next, set a timer for 5 minutes.
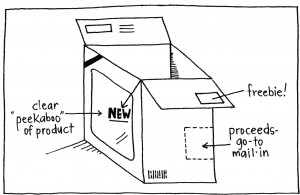
5. Tell the players to sit silently and sketch out as many ideas as they can until the timer ends — with the goal of reaching 6-8 ideas. The sketches can and should be very rough — nothing polished in this stage.
6. When the time runs out, the players should share their sketches with the rest of the group. The group can ask questions of each player, but this is not a time for a larger brainstorming session. Make sure every player presents his/her sketches.
7. With time permitting, repeat another few rounds of 6-8-5. Players can further develop any ideas that were presented by the group as a whole or can sketch new ideas that emerged since the last round. They can continue to work on separate ideas, or begin working on the same idea. But the 5-minute sketching sprint should always be done silently and independently.
Strategy
6-8-5 is intended to help players generate many ideas in succession, without worrying about the details or implementation of any particular idea. It’s designed to keep players on task by limiting them to sketch in small boxes and work fast in a limited amount of time. 6-8-5 can be used on any product or concept that you want to brainstorm, and have the best results with a heterogenous group (people from product, marketing, engineering, design…).
6-8-5 works great in the early stages of the ideation process, and are often followed by a debrief and synthesis session or by another gamestorming exercise to identify the most fruitful ideas given the team’s business, product, or end-user goals.
6-8-5 has been used in design studio workshops for rapid ideation. This game is credited to Todd Zaki Warfel.